By Michael Rank
North Korea’s orphanages are full of malnourished children and food shortages in the isolated nation look set to get much worse, said a recent visitor who knows the country well.
Former member of the European Parliament Glyn Ford said shortages of food were affecting “tens of thousands of children, not just orphans, and there may be millions of people under threat of malnutrition” in North Korea.
Ford visited two orphanages in Hamhŭng (Hamheung), the country’s second largest city, where he was shown children who were extremely thin and clearly malnourished, and this had been confirmed by a European Union aid team. Each orphanage had about 300 children.
Ford said he had been encouraged by an EU pledge last month to provide emergency food aid worth 10 million euros ($14.3 million) to more than half a million people at risk of dying from serious malnutrition in North Korea, and that France and Germany had since added to this, making the assistance worth 14-16 million euros ($20-$22.8 million).
But at one of the orphanages he was told they had run out of EU food in June, and the children were suffering as a result.
The European Commission said the objective of the aid package was to lift around 650,000 people, mainly in northern and eastern provinces of the country, out of the hunger zone during the most difficult period of the worst year for food production in recent times. Food assistance will reach children under five who have already been hospitalised with severe acute malnutrition. Children in residential care will also be fed, as well as pregnant and breastfeeding women, hospital patients and the elderly.
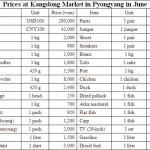
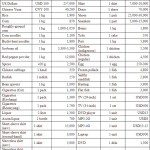
An EU mission found in June that state-distributed food rations, upon which two thirds of the North Korean population depend, had been severely cut in recent months from 400g of cereals per person per day in early April to 150g in June: less than 400kCal – a fifth of the daily average nutritional requirement and equivalent to a small bowl of rice.
Ford told NKEW in a telephone interview that while there were clear signs of widespread hunger there was no sign, so far at least, of mass starvation, as happened in the 1990s, when hundreds of thousands, possibly millions, of people died.
He also said that despite the food shortages there were also signs that economic reforms of recent years were having a strong impact, and that in all populated areas roads were lined with rows of private stalls. “These blue plastic stalls are everywhere,” Ford said, adding that they were giving rise to
“kiosk capitalists” who were bucking the traditional, Stalinist economic system.
“This is a society where there are rich North Koreans. There are new cars and expensive consumer items in the shops. There is an economic elite rather than a Party elite,” he added.
Ford also visited the Kaesong (Gaeseong) Industrial Complex just north of the Demilitarised Zone, which he said consisted of large areas of waste land where plans for expansion had come to nought due to increased tension between North and South Korea.
The complex looked “a little bit sad”, he said, and the optimism that prevailed when he last visited it two or three years had dissipated. He said the zone continued to employ about 45,000 North Koreans, little changed from his previous visit, and hopes that it would employ 400,000 by 2015 now seemed highly unrealistic. “It was new then but the shining glow has gone off a bit,” he said, adding, “I noticed the gaps between the factories more than the factories themselves.” (Ford cited a goal of 400,000 workers eventually employed in the zone, but in 2006 a target of 700,000 was mentioned on the BBC’s Newsnight programme).
The complex, in operation since 2004, has around 120 factories, all South Korean-run, processing food and assembling clothing and machinery for export to the South.
Ford also said it seemed likely that the North Korea would open an embassy to the EU in Brussels before long, with a reciprocal EU embassy in Pyongyang. Although Pyongyang and the EU established diplomatic relations in 2001, embassies have not been opened due to French resistance, as France and Estonia are the only EU countries that do not have full diplomatic ties with North Korea.
France has cited human rights violations in its refusal to open an embassy in North Korea, but it has recently softened its line and has announced plans to open a “cooperation bureau” in Pyongyang. Ford said North Korea had long wanted to set up an embassy in Brussels and this now finally seemed likely, possibly by the middle of next year.
Ford, a British Labour Party MEP until 2009, spent about 12 days in North Korea, returning last Saturday. He has almost certainly visited North Korea more often than any other western politician, having been almost 20 times over the last 15-16 years. He was a member of the European Parliament’s Korean Peninsula delegation and in 2008 has published a book, North Korea on the Brink: Struggle for Survival.
Addendum: In January 2009 Ford hosted the first ever delegation from the Workers’ Party of Korea (WPK) delegation to visit Britain, when he pressed them to agree to reopen the dialogue that was broken off in 2005.