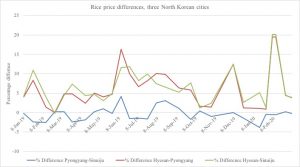
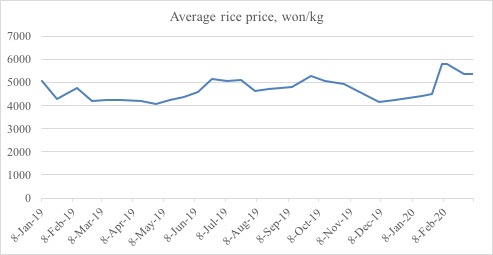
By: Benjamin Katzeff Silberstein
On Saturday February 29th, the Political Bureau of the Central Committee of the Korean Worker’s Party held a so-called “enlarged” meeting. According to the KCNA report, the meeting dealt primarily with purges of corrupt officials, and coronavirus measures:
At the enlarged meeting acts alien to the party, abuse of power, practices of privileges, indulgence in bureaucracy, corruption and irregularities revealed among senior officials of the Party Central Committee and officials of the Party cadre training institution were harshly criticized and their gravity and consequences were sharply analyzed.
The Supreme Leader clarified the analysis of the issues by the Party Central Committee and its stand on them, and dealt strong blows at the acts alien to the party and unpopular and anti-socialist acts brought up for discussion at the meeting. He called on all the Party officials and organizations to draw a serious lesson from the recent incident, to make steady efforts to revolutionarize themselves and their units and bring about a new turn in the Party work.
The Political Bureau of the Party Central Committee dismissed Ri Man Gon and Pak Thae Dok from the posts of vice-chairmen of the Party Central Committee.
The meeting adopted a decision to disband the party committee of the Party cadre training base which was involved in the practices of corruption and irregularities, and to impose relevant penalty.
It’s not clear precisely what “strong blows at the acts alien to the party and unpopular and anti-socialist acts”, but presumably it refers to corruption. Corruption is one of the most common acts for WPK-officials to get purged (or fired) over, and the formulations indicate that this is indeed what happened here. Some have suggested it may have had to do with shoddy work in the country’s coronavirus measures, but even reading carefully between the lines, I can’t see enough evidence to back that up. “[A]cts alien to the Party” [비당적 적행위], I would argue, is a clear statement about specific acts particularly alien to the Party’s values. Shoddy handling of specific policy implementation related to the virus does not fall naturally into that category. Moreover, the antivirus measures were praised at the very same meeting. North Korean politics is full of contrasts and mixed messages, but this would be a stretch too far.
The problem with these methods, of course, is that they do nothing to address the long-term issue of corruption. The WPK (and the North Korean state for that matter) lacks institutions for accountability and independent oversight. There is no proper justice system in any reasonable sense of the term. So scare campaigns and setting examples, like the CC meeting in question did, really is the only avenue available. These measures might have some positive impacts in the short run – we don’t know – but in the long run, they make little difference. Kim Jong-un has ostensibly made anti-corruption a priority, but so far, campaigns and sporadic crackdowns are the only visible results. Corruption is obviously bad for the economy, but if it helps people get around draconian laws (as is the case in North Korea) to do business, it might be a net positive for the economy.
The meeting also dealt with North Korea’s efforts to contain the coronavirus. There’s a lot to say about the text, I’ve highlighted (in bold) the part relating to economic affairs:
Discussed at the meeting were issues of taking nationwide top-class anti-epidemic steps in a more thorough-going way and strictly putting them into practice in order to cope with the viral epidemic spreading rapidly around the world.
In case the infectious disease spreading beyond control finds its way into our country, it will entail serious consequences, the Supreme Leader said, noting that the strong measures taken by our Party and the government from the beginning have been the surest and highly reliable, preemptive and decisive preventive measures as this viral infection spreads so rapidly, its incubation period is uncertain and its contagion route is also scientifically uncertain.
An urgent task at present is to supplement and complement the law on the state emergency anti-epidemic and to readjust state crisis control regulations in an orderly way, the Supreme Leader said, emphasizing that the Presidium of the Supreme People’s Assembly, the Cabinet and other related institutions must further strengthen the state anti-epidemic force immediately and push ahead with the work for supplementing and complementing anti-epidemic means, system and laws based on the experiences gained through the on-going enforcement of preemptive and powerful anti-epidemic measures to cope with infectious disease.
The enlarged meeting also discussed measures to deter the influx and spread of the infectious disease in a scientific, preemptive and lockdown way.
No special cases must be allowed within the state anti-epidemic system, the Supreme Leader said, stressing the need to set up a strict discipline by which all the fields and units of the country unconditionally obey to the command and control of the Central Headquarters for the emergency anti-epidemic work and thoroughly execute instructions from it, and to further tighten the system of reporting to the Party and legal surveillance.
He instructed the Cabinet and the Central Emergency Anti-epidemic Headquarters to seal off all the channels and space through which the infectious disease may find its way, and strengthen check-up, test and quarantine under the work system and order already in place.
The meeting also stressed the issue of tightening economic organization and anti-epidemic work under the prevailing situation and conditions so as to accomplish this year’s goals without fail and to thoroughly ensure the life and security of the people.
It is important for the Party organizations at all levels to have clear understanding of the intention of the Party Central Committee and put it into practice, the Supreme Leader said, urging the need for the Party to provide an impetus so that the Cabinet and the economic institutions at all levels could provide proper economic operation and command under the present situation.
The anti-epidemic measures being taken by us is a crucial state affair for the defence of the people and a heavy responsibility of the Party Central Committee, not just the prevention of the disease, the Supreme Leader said, underlining the need for all to thoroughly carry out the decisions and instructions of the Party Central Committee and direct all-out efforts to the security of the country and the life and safety of the people.
The question is, of course, what this means in practice. There is no doubt that the economy is suffering, and not just in terms of sheer growth numbers or the like. Much of North Korea’s imports from China are blocked due to the border closure, and even smuggling is facing heavy clampdowns. Internal travel and movement of goods is heavily restricted. There is, it seems to me, fairly little that the state can really do to balance this all in terms of economic measures, but of course, the state must tell the population that it is doing things and taking action.
(Source: Korean Central News Agency, “Enlarged Meeting of Political Bureau of C.C., WPK Held,” 29/2/2020.)