UPDATE 14 (2016-12-8): The Pyongyang Times reports on the CDM project:
Various CDM projects obtain CERs
The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change CDM Executive Board recently issued certified emission reductions for the DPRK’s clean development mechanism projects.
Today many countries make great efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions as part of the worldwide bid to prevent global warming, the root cause of climate change.
The DPRK also proactively joins in the international efforts.
It signed the Kyoto Protocol, which took effect in 2005, and joined the Paris agreement on climate change signed by 174 countries in August this year.
The agreement, adopted at the UN Conference on Climate Change in Paris in 2015, is aimed at reducing the world’s greenhouse gas emissions to the maximum so that the global average temperatine would not rise more than 2 degrees over that in the 1850s, the pre-industrialization period.
As a signatory to the Paris agreement, the DPRK has worked out 2024 and 2030 greenhouse gas reduction plans and pushed ahead with them.
In keeping with the trend when the sales of carbon dioxide emission rights have emerged as CDM and CDM activities are brisk in the world environmental protection market, a non-permanent CDM committee has been set up in the Cabinet and the General Bureau for Cooperation with International Organizations of the Ministry of External Economic Relations plays the role of its secretariat.
While coordinating all CDM project activities in the country, the secretariat also undertakes issuance of CERs for various CDM project activities on the basis of agreements on cooperation for the development of CDM projects with CER buyers, Topic Energo of the Czech Republic and Ohana LLP, Britain.
In the course of this, several projects were registered as CDM projects by the CDM Executive Board. They include Ryesonggang Youth Power Station units 3, 4 and 5, Hamhung Youth Power Station unit 1, Kumyagang Power Station unit 2, Paektusan Hero Youth Power Station unit 2 and package projects for “Treatment of waste water from chemical factories in the DPRK” and “Collection and use of methane gas from coal mines in the DPRK”.
The secretariat ensured that Paektusan Hero Youth Power Station unit 2 and Ryesonggang Youth Power Station unit 4 obtained CERS for the first time after receiving international certification for their power generation in May.
Their CERs issued amount to 15 800 and 27 807 tons respectively.
The secretariat now works to achieve international certification of other registered CDM projects.
By Jong Hwa Sun PT
UPDATE 13 (2014-11-28): The Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No.4 has been completed. According to KCNA:
New Power Station Goes Operational
Kumchon, November 27 (KCNA) — Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 4 went operational.
President Kim Il Sung indicated the orientation of building the power stations on the Ryesong River. Leader Kim Jong Il visited the construction sites several times, setting forth tasks and ways for the construction and bestowing loving care and benevolence on the builders.
Marshal Kim Jong Un appreciated the achievements of the people in North Hwanghae Province when he visited Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 1. He not only took measures for finishing the construction of Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 2 by the concerted efforts of the army and people but also led the construction of Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 4.
The completion of Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 4 is another success in implementing the behests of Kim Il Sung and Kim Jong Il to settle the acute shortage of electricity in the North Hwanghae Province by building power stations on the Ryesong River. It also helped lay a more solid foundation for developing economy and improving the living standard of the people in the province.
The completion ceremony took place on Thursday.
Present at the ceremony were Tong Jong Ho, minister of Construction and Building-Materials Industry, Pak Thae Dok, chief secretary of the North Hwanghae Provincial Committee of the Workers’ Party of Korea, and others.
Here is KCTV footage (7:21). Here is UNFCCC data.
UPDATE 12 (2012-12-13): Robert Winstanley-Chesters has some additional data here.
UPDATE 11 (2012-11-25): The DPRK has registered four more power plants with the UNFCCC CDM project.
1. Paekdusan Songun Youth Power Station No. 2 (백두산선군청년2호발전소)
Registered July 13, 2012
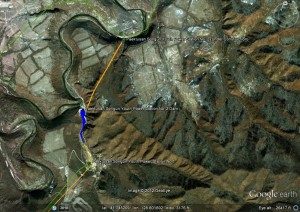
Pictured Above (Google Earth): The approximate location of the Paekdusan Songun Youth Power Station No. 2
The UNFCCC documents on the registration of the power plant can be seen here.
Total installed capacity of the project will be 14 MW, consisting of two sets of 7 MW hydropower turbines and associated generators.
According to the UN documents, the project is expected to be put into operation on January 1, 2014.
The organizations listed on the document are the Namgang Hydropower Construction Complex and Topič Energo s.r.o. (Czech Republic)
2. Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 4 (례성강청년4호발전소)
Registered July 20, 2012
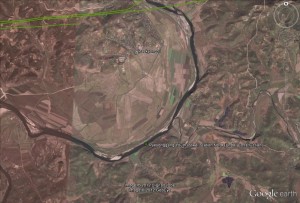
Pictured Above (Google Earth): The approximate location of the Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 4.
The UNFCCC documents on the registration of the power plant can be seen here.
The installed capacity of the project is 10 MW, which consists of 4 sets of generating facilities with a capacity of 2.5 MW each. The project will generate the electricity energy of 40,030 MWh and supply 38,640 MWh to the WPG in a year.
According to the UN documents, the project is expected to be put into operation on December 1, 2012. This facility was last featured on the DPRK evening news on 2012-11-8. See the footage here.
The organizations listed on the document are the Kumchon Electric Power Company and Topič Energo s.r.o. (Czech Republic).
3. Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 5 (례성강청년5호발전소)
Registered August 22, 2012

Pictured Above (Google Earth): Construction work on the Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 5.
The UNFCCC documents on the registration of the power plant can be seen here.
The installed capacity of the project is 10 MW, which consists of 4 sets of generating facilities with a capacity of 2.5 MW each. The project will generate electric energy of 41,150 MWh and supply 40,616 MWh.
Organizations listed in the document include the Kangdong Hydro Power Construction Company and Topič Energo s.r.o. (Czech Republic).
According to the documents, the project is planned to be put into operation on May 1, 2012. The most recent Google Earth satellite imagery is dated Spetember 5, 2011 and the last time the project was featured on North Korean television was November 5, 2011. I am skeptical that the project was finished on time since the opening of the dam has yet to be announced publicly.
4. Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 3 (례성강청년3호발전소)
Registered October 23, 2012

Pictured Above (Google Earth): Construction work on the Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 3.
The UNFCCC documents on the registration of the power plant can be seen here.
The project with an installed capacity of 10 MW, 4 sets of generating facilities with a capacity of 2.5 MW
respectively. The project will generate the electricity energy of 42,800 MWh and supply the electricity of 41,310
MWh.
Organizations listed in the document include the Tosan Electric Power Company and Topič Energo s.r.o. (Czech Republic).
Though the plant is supposed to go into operation on July 1, 2012, the most recent Google Earth imagery from 2012-11-8 shows the plan remains uncompleted. The last time the plant was featured on North Korean television was 2011-6-25.
UPDATE 10 (2012-10-23): The DPRK has registered its second CDM project: Kumya Hydro Power Plant. (AKA Kumyagang Power Station No. 2, 금야강2호발전소)
Here is the official UN web page containing all of the technical information.
Here is a Google Earth satellite image featuring the dam and power station (39.552132°, 127.156062°):

The Hanns Seidel Foundation (Facebook page here) visited the site and took this photo:

KCTV footage dated 2014-9-16 shows a completed Kumya Hydro Power Plant (AKA Kumyagang Power Station No. 2). See the footage here.
UPDATE 9 (2012-8-16): The DPRK’s first CDM project registered: Hamhung Hydro Power Plant No. 1 (AKA Hamhung Youth Power Station No. 1)

Pictured above (date unknown): On Bing Maps (coordinates: 39.648086°, 127.269219°) we can see construction is underway
A valued reader notified me this morning that the DPRK’s first CDM project was registered in July: The Hamhung Hydro Power Plant No.1.
You can read more about the project on the UN web page here. As I understand it, the CER (the emissions rights) from the plant do not go directly to North Korea but to a Czech company who co-registered the project. It will become operational on January 1, 2013.
UPDATE 8 (2012-6-5): In addition to the seven power plants submitted for approval below, the DPRK is involved in several other “Programmes of Activities (POAs)“. You can see all the POAs by clicking here and selecting DPRK as “Host Country”.
Here is a summary:
1. Methane Utilization and Destruction Programme from Animal Waste Management System (AWMS) in DPR Korea
2. Methane Utilisation and Destruction Programme from Industrial Wastewater in DPR Korea
3. CarbonSoft Open Source PoA, LED Lighting Distribution: Emerging Markets
4. Coal Mine Methane Utilisation and Destruction Programme in DPR Korea
5. International water purification programme
6. CFL Lighting Scheme in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK)
UPDATE 7 (2012-6-2): The creator of Nord Korea Info passed along the following information on the DPRK’s CDM projects:
1. Naenara, one of the DPRK’s official news outlets, has posted numerous CDM documents. You can see them here.
2. Information posted to the UNFCCC web page on specific CDM projects:
A. Kumya Hydropower Plant (AKA Kumyagang Power Staiton No. 2)
B. Ryesonggang Hydropower Plant No.3 (Comments) (AKA Ryesonggang Youth Power Station N. 3)
C. Ryesonggang Hydropower Plant No.4 (Comments) (AKA Ryesonggang Youth Power Station N. 4)
D. Ryesonggang Hydropower Plant No.5 (Comments) (AKA Ryesonggang Youth Power Station N. 5)
E. Paekdusan Songun Youth 14MW Hydropower Project No.2 (AKA Paektusan Songun Youth Power Station No. 2)
F. Wonsankunmin Hydropower Project No.1 (Comments) (AKA Wonsan Army People Power Station No. 1)
G. Hamhung Hydropower Plant No.1 (AKA Hamhung Youth Power Station No. 1)
No new information is available on the Hamhung 20MW Hydropower Plant No. 2 (AKA Hamhung Youth Power Station No. 2). So I am unsure what has happened to it.
UPDATE 6 (2012-5-31): Bloomberg Businessweek reports on the DPRK’s efforts to sell carbon credits:
[U]nder the terms of the [Kyoto] protocol, North Korea, as a developing country and a member of the United Nations, has the right to build clean energy projects that may apply for Certified Emission Reductions, or CERs, popularly known as carbon credits. The North Koreans can then sell them to a rich country or company that needs the credits to offset its own greenhouse gases. Dig into data from the UN’s Framework Convention on Climate Change, and you will find seven North Korean projects registered for carbon trading.
This is where Miroslav Blazek comes in. Blazek, director of Czech company Topic Energo, acts as a link between North Korea and potential carbon credit buyers. He says his experience as manager of a tractor factory in socialist-era Czechoslovakia is invaluable for doing business with the communist North Koreans. “I can work with them because I understand how their system works,” he says. “If I send an e-mail and still don’t have a reply in several days, I know it’s not because they didn’t see it but because it had to work its way through the chain of command. For me it’s like a trip down memory lane.”
North Korea is now building seven hydroelecrtric plants, which provide some of the cleanest energy going. Most can earn tradable carbon credits. Blazek says the North Koreans “jumped” at the opportunity to get into carbon trading: “They immediately grasped that this is a way to make money.” Korea’s seven dams may generate as many as 241,000 CERs a year, worth almost €1 million ($1.3 million). “The projects are already in a relatively advanced phase,” says Ondrej Bores, director of carbon advisory services at Virtuse Energy in Prague, who’s worked with Blazek on other deals.
Still, selling anything made in North Korea has its challenges. More than 30 potential buyers pulled out because of the U.S. embargo on trade with North Korea. Blazek finally struck a deal with a Chinese-controlled conglomerate that needs credits to offset emissions from facilities in Europe. He won’t name the company, citing a confidentiality clause.
The Prague Post also reported on this story.
UPDATE 5 (2012-2-14): I have been notified that the certification program is proceeding. From a reader:
There has been a statement by the 1718 committee (on sanctions) that CDM projects in NK do not violate UN rules.
[Seven] hydropower plants did get their validation and underwent a process of “clarifications and corrections” as foreseen by UN rules. After the final report (which might have been already issued or might be issued soon) they will go for final vote to the UNFCCC.
Currently, North Korea works on projects as diverse as methane gas from coal mines, bio-gas and electricity-saving light bulbs.
UPDATE 4 (2011-7-11): I just checked the UNFCCC web page, and it appears that in addition to the hydro power plants mentioned below, the North Koreans also submitted the “Energy Efficiency Improvement Project in Pyongyang Textile Factory” [sic] for carbon offsets on May 23, 2011. According to the UNFCCC web page, the project is in the portfolio of the Carbon-Trade Division, GBCIO, Ministry of Foreign Trade.
UPDATE 3 (2011-7-11): DPRK begins construction of Ryesonggang Power Stations 3 and 4
On June 25th the DPRK evening news featured footage of the construction of the Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 3 (례성강청년3호발전소). I have uploaded the footage to YouTube and you can see it here.
On June 28th the DPRK evening news featured footage of the construction of the Ryesonggang Youth Power Station No. 4 (례성강청년4호발전소). I have uploaded the footage to YouTube and you can see it here.
UPDATE 2 (2011-3-11): The DPRK has apparently registered eight power plants with the UNFCCC. According to Reuters:
North Korea has registered eight hydroelectric plants with the United Nations, and if approved, could allow the world’s most reclusive state to sell carbon offsets to earn precious hard currency.
These hydropower projects were registered with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) for prior consideration in getting carbon credits, some of which have a capacity of 20 megawatts, the UNFCCC website showed.
Prior consideration is the first step for accreditation toward the U.N.’s Clean Development Mechanism that allows developing countries to earn tradeable carbon credits for emissions from clean-energy projects.
Bernhard Seliger, a messenger for North Korean officials on these projects, said the United Nations uploaded the information on Thursday after he submitted related forms on behalf of the North Korean government’s carbon trade division in late February.
“I have no idea when the U.N. makes a decision… North Korea has to finish the power plants, which up to now are only half-finished dams,” Seliger, Hanns Seidel Foundation’s representative in South Korea, told Reuters via email.
Analysts questioned the demand for carbon credits from North Korea, concerned the money might be siphoned off to nuclear arms or other military projects.
According to the UNFCCC web page (select Democratic People’s Republic of Korea in the “Host Party” box), these are the eight power stations that have been submitted for consideration:
Hamhung Hydropower Plant No.1 (AKA Hamhung Youth Power Station No. 1)
Hamhung 20MW Hydropower Plant No. 2 (AKA Hamhung Youth Power Station No. 2)
Kumya Hydropower Plant (AKA Kumyagang Power Station No. 2)
Paekdusan Songun Youth 14MW Hydropower Project No.2 (AKA Paektusan Songun Youth Power Station No. 2)
Ryesonggang Hydropower Project No. 3 (AKA Ryesonggang Youth Power Station N. 3)
Ryesonggang Hydropower Project No. 4 (AKA Ryesonggang Youth Power Station N. 4)
Ryesonggang Hydropower Project No. 5 (AKA Ryesonggang Youth Power Station N. 5)
Wonsangunmin 20MW Hydropower Project No. 1 (AKA Wonsan Army People Power Station No. 1)
And according to an email from the UNFCCC:
This list contains all the projects which have already started and for which a notification of CDM prior consideration has been submitted. This notification is necessary to prove that the incentive of the CDM was a decisive factor for taking up the project when a project has started before a project design document (PDD) has been published for global stakeholder consultation or a new methodology in connection with the project has been submitted. However, kindly note that these projects have not yet entered the CDM project cycle as lined out in the CDM rules, requirements and procedures, and to submission for registration has yet been made.
Further details on the CDM project cycle are available here: http://cdm.unfccc.int/Projects/diagram.html
UPDATE 1 (2011-3-8): According to the Guardian:
North Korea hopes to earn much-needed hard currency by selling UN-backed carbon offsets from a series of hydro-power projects, as the country faces sanctions over its nuclear weapons programme.
If approved and registered by the UN, these would be the first projects for North Korea under a scheme called the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM). This allows developing countries to earn tradeable carbon credits for emissions reductions from clean-energy projects.
Some analysts questioned the demand for carbon credits from North Korea, with fears the money might be siphoned off to nuclear arms or other military projects.
The government has asked the Hanns Seidel Foundation of Germany, which focuses on humanitarian issues, to act as a go-between by working with UN-approved verification agency TUV Nord.
According to Bernhard Seliger, the foundation’s representative in South Korea, North Korea is initially looking at trying to get approval for three hydro power plants of 7-8 megawatts (MW).
Seliger visited the three hydro-plant construction sites in the north-east corner of the country in January.
In a statement, TUV Nord confirmed the foundation had engaged their services.
“In this respect, TUV Nord intends to verify hydropower dams in North Korea once pre-registered with United Nations framework conventions on climate change [UNFCCC] via the Beijing branch of its Chinese subsidiary TUV Nord Guangzhou,” it said.
If registered, the plants could yield millions of euros over several years.
Beijing-based lawyer Tom Luckock, who specialises in projects that curb greenhouse gas emissions, estimated that an 8 MW hydro plant could yield about 23,000 UN offsets a year.
The offsets, called Certified Emissions Reductions (CERs), are generated from registered CDM projects, such as wind farms, that are rewarded for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The offsets currently trade at nearly €12 (£10) each and are bought by governments in rich nations that need to meet UN emissions reduction targets.
Europe is the biggest buyer, with large polluting firms allowed to buy the offsets to meet a portion of their emissions reduction targets under the EU’s emissions trading scheme.
“Finding ways to secure foreign currency is the priority for North Korea, which is linked to everything from food to raw material imports to boost reduced productivity,” said Cho Myung-chul, a senior researcher at the Korea Institute for International Economic Policy.
…
Seliger said North Korea, which signed the UN’s Kyoto Protocol climate pact in 2005, was also interested in biomass power generation projects under the CDM.
The UN-approved national agency that assesses and approves CDM projects in North Korea was not available for comment.
Questions remained on demand for North Korean CERs.
“Even if they open up, who in the world wants to pay for North Korea that is blamed for its nuclear weapons programme?” said Choi Soo-young, a senior researcher at the Korea Institute for National Unification.
Cho said the UN needed to prevent outside cash going into its nuclear development activities, while Luckock, of global law firm Norton Rose, said: “Their limited access to hard currency has to be a concern for buyers – the damages clauses will carry limited weight without some security there.”
Another challenge is that North Korea would have to make public its energy consumption and generation data and disclose information on the amount of energy linked to the hydro project.
“Annual inspection, constant measurement and energy flow posting on the [UNFCCC] website – all these things are new for North Korea,” Seliger said.
According to the AFP:
“We are talking about eight power plants, with the smallest size about 7.5 megawatts. These are not big projects but small or medium-sized projects,” Bernhard Seliger told AFP.
None has yet been completed, he said.
“I saw some (construction) sites in South Hamkyong province but that’s not all. There are other plants in other regions,” Seliger said, adding that some of the projects are led by the UN Development Programme.
The Hanns Seidel Foundation has been working since 2003 to build the North’s development capacity, and in 2008 organised a seminar on carbon trading for Pyongyang officials at their request.
The tradeable credits, called Certified Emissions Reductions, are awarded for approved clean-energy projects such as hydropower plants or wind farms.
Big polluters elsewhere in the world can buy them as part of their efforts to cut emissions.
Seliger said his foundation is helping the North to prepare for the auditing process required to join the UN carbon credit trading system known as the Clean Development Mechanism.
“One good thing about this project is that it is very transparent, involving monitoring and auditing on an annual basis… I think it is very good for North Korea to participate in such an international regime,” said Seliger.
An official at a South Korean state agency, the Korea Energy Management Corp, said registration would take at least a year or two and it was unclear how much the North would be able to earn if approved.
The official, who declined to be identified, said a typical eight-megawatt hydropower plant could yield about 19,500 carbon credits each year, each of which was currently traded at 12 euros in global markets.
This would amount to around $327,000 a year.
But some buyers may shun the communist state, given its history of nuclear and missile development which has led to international sanctions.
“Government buyers will certainly shy away from dealing with the North,” said Koo Jung-Han, a researcher at the Korea Institute of Finance.
“But private companies have few reasons not to buy credits from the North as long as it can offer a competitively low price. However, the big question is whether the North will be able to build the plants without outside financiers.”
Koo said that countries hoping to buy carbon credits from upcoming overseas projects often encourage investment in the ventures by their own finance companies.
“But what kind of financial companies will take a plunge in projects in such a volatile, politically risky country like North Korea?”
The North suffers persistent power shortages even in the showpiece capital Pyongyang.
Many rural areas receive power only during key agricultural seasons, and must rely for the rest of the year on alternative fuels, according to a recent policy paper published by the Nautilus Institute think-tank.
Here are the web pages for the Hanns Seidel Foundation and the UNFCCC Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) Program.
A reader writes in with the following comments:
I would like to share some comments on the potential CDM projects in north Korea as i have been working on this field for many years now.
Concerning existing hydro-power plants:
To be eligible as a CDM project, one of the first criteria is the additionality of the project. You have to prove (the rules are very strict) that the project would not have been launched without the consideration of the revenues from the reselling of the CERs. So the dams that have already been buit are not eligible.
Concerning hydro-power plants that are being implemented:
The first step of a CDM project is to notify to the UNFCCC secretariat and to Designated National Authority (in this case the Secretariat of the National Coordinating Committee of Democratic People’s Republic of Korea for Environment) that you are seeking to establish your project as a CDM project. Up to now, no such notification has been received by UNFCCC so it would be quite difficult for projects being implemented to ask for the CDM status (I mean nearly impossible).
Some facts concerning future hydro-power projects:
From the day you send the notification that you are seeking the CDM status to the day you are actually given the status, it takes in average 2 to 3 years (they would have to build the plants during this period). Then it can be at least another year before you receive the CERs. The price of 12 euro for a CER is for secondary market. The price for primary CER (directly sold by the producer) would be much less than 8 euro.
The figure of 20 000 CERs/year is completely unpredictable for the moment, here is a simplification of the calculation: One CER is equal to one tonne of CO2 equivalent that would be avoided by producing clean electricity. For example when you produce 1 MW electricity from coal, the process releases X tonnes of CO2 in the atmosphere but when you produce 1 MW from a hydropower plant, you do not release CO2. In order to calculate what the CDM project would be able to claim, we would have to know the CO2 emission factor of the North Korean grid and then multiply it by the amount of MWh produced by the CDM project. If most of the electricity produced these days in North Korea already comes from hydro-power plants, then the national emission factor will be low and the CDM project will not avoid a lot of CO2 emission (and so not earn a lot of €) Without the capacity of the future project and the national emission factor, it is impossible to estimate the amount of CERs the project could generate.
The CDM status seems quiet unrealistic to obtain for North Korean projects but other international agreements are discussed these days and their outcome may be more adapted.
ORIGINAL POST (2011-1-31): According to Radio Free Asia:
Nuclear-armed but cash-starved North Korea has expressed interest in joining the world carbon market in an apparent bid to earn precious hard currency and avoid international sanctions, an expert told RFA.
But the secretive Kim Jong Il regime has to disclose critical information, such as energy consumption data as well as methods by which it derives energy, to be eligible for funding under the United Nations’ Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), said the North Korea expert, speaking on condition of anonymity.
The CDM is aimed at encouraging companies or organizations in the developed world to invest in carbon dioxide emissions-saving projects in developing countries.
In return for funding and technology transfer, investors receive carbon credits, which can then either be traded on carbon markets or used to reduce their own emissions tally if they are subject to a domestic cap.
The Kyoto Protocol set emission caps for 38 countries through 2012, establishing the CDM as a worldwide carbon market. It is a cornerstone of the group’s efforts to tackle global warming.
The North Korea expert told RFA on Jan. 13 that Pyongyang intended to apply for funding via the CDM and that the regime might list its proposed hydro-electricity power projects under the U.N. mechanism.
UN refrains from comment
When contacted on the North Korea move, the U.N. Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the secretariat charged with implementing the global environmental treaty to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations, said it would refrain from commenting on individual country projects.
The North Korea expert estimated that one ton of carbon dioxide would trade for about U.S. $26 dollars and if a hydro-electric power project was registered under the CDM, depending on the carbon credit bid price, about U.S. $1 million dollars could be earned annually.
A hydro project registered under the CDM would need to be evaluated by U.N. inspectors for it to qualify for carbon credits. Usually, it would be evaluated continuously for about 14 years.
Details, including the amount of energy linked to the hydro project and potential reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, would have to be submitted.
North Korea has been mostly reluctant to share information about its energy generation activities.
According to the expert, North Korea has recently displayed “great interest” in the possibility of operating hydro-electric power stations to alleviate its domestic energy shortages and to acquire “carbon credits” that it could, in turn, sell on the international carbon market.
Hard currency
As North Korea’s economic crisis worsens, Pyongyang is seeking ways to earn hard currency following a failed currency reform and due to sanctions imposed by the international community over its nuclear and missile developments and provocations targeting South Korea.
The interest in the CDM is likely to be part of this search.
The North Korea expert also said that earning hard currency through “carbon credits” would not be subject to sanctions imposed on Pyongyang under UN Security Council resolutions, and that any North Korea’s application for participation under the CDM “may stand a chance.”
“For North Korea, this could be an opportunity to earn hard currency without engaging in illegal armament sales, while operating an electric power station in transparent fashion, and accepting strict monitoring by the UN, and abiding by applicable international standards.”
The United States has been pressing China to use its influence to persuade North Korea regime to end recent provocations and return to disarmament talks involving the three countries and South Korea, Russia and Japan.
The six-party nuclear talks were last held in 2008. The impoverished North has been seeking a restart to the nuclear negotiations, which propose to reward its gradual nuclear disarmament with phased infusions of economic aid.
In a bid to renew dialogue and ease chances of conflict, South Korea recently proposed holding a preliminary meeting with North Korea on Feb. 11 to prepare for high-level defense talks. On Friday, the North suggested parliamentary talks between the two sides.
Read the full story here:
North Korea Eyes Carbon Market
Radio Free Asia
1/29/2011








