UPDATE 6 (2011-4-20): The DPRK is experiencing a new wave of foot and mouth outbreaks. According to Yonhap:
A new outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) occurred in four counties in North Korea last month and infected nearly 300 pigs and cows, a news report said Wednesday.
A total of 141 out of 298 animals died after being infected with the disease, the Voice of America said, citing a North Korean report submitted to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) on Monday. The news report said Pyongyang quarantined the infected areas in an apparent attempt to stem the spread of the disease.
The North confirmed its first case of the disease in December, and the virus has since spread to six other cities and provinces, Seoul’s Agriculture Minister Yoo Jeong-bok said in February.
Last month, the World Organization for Animal Health said North Korea urgently needed around US$1 million worth of equipment and vaccines to help stem outbreaks of the deadly disease.
The disease does not pose a direct health threat to humans, but affects cows, sheep, goats and other cloven-hoofed animals, causing blisters on the nose, mouth, hooves and teats.
North Korea has 577,000 heads of cattle, 2.2 million pigs and 3.5 million goats, according to the OIE.
The OIE data mentioned in the above Yonhap story can be found here.
The OIE provides the map below as well as details about the outbreaks:
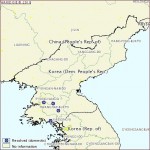
Three of the four cases take place in North Hwanghae:
Sinphyong county, Myongri district (2011-3-21)
Sangwon county, Rodong-ri (2011-3-16)
Hwangju county, Ryongchon-ri (2011-4-4)
The final case is in Singyo-ri, Kumgang County, Kangwon Province. It reportedly took place on 2011-4-6.
The data is also available here.
UPDATE 5 (2011-3-24): UN FAO Press Release:
North Korea: FAO says urgent vaccine and equipment needed to contain Foot-and-Mouth Disease
Capacity of national veterinary services to manage animal disease must also be strengthened
24 March 2010, Rome/Paris – Around a million dollars of equipment and vaccines are urgently required to help stem outbreaks of deadly Foot-and-Mouth disease (FMD) in North Korea, followed by a more prolonged and concerted effort to modernize veterinary services in the country.
A joint FAO and World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) mission travelled to North Korea at the government’s request between 27 February and 8 March. The mission found that the country’s capacity and that of veterinary services to detect and contain FMD outbreaks need significant strengthening — in particular as regards implementing best-practices in biosecurity measures and improving laboratory infrastructure and capacity.
Outbreaks of Type-O FMD have been reported in diverse locations in eight of North Korea’s 13 provinces. To bring the situation under control, the team recommended the following steps:
- Thorough surveillance to locate and map disease clusters
- Protecting unaffected farms through movement controls and biosecurity measures
- Adequate sampling in order to correctly identify the virus strain or strains involved
- Improving biosecurity measures to prevent further spread of the disease
- The strategic use of the appropriate vaccines to contain and isolate disease clusters
FAO estimates around $1 million is required immediately for training, supplies and infrastructure, vaccine acquisition and the setting up of monitoring, reporting and response systems.
The FAO-OIE mission visited several collective farms as well as the national veterinary laboratory and various animal health field stations.
Virus identification
FAO and OIE provided guidance to North Korean veterinary authorities on taking and handling of FMD samples — new samples will be collected by North Korea and sent to an international reference laboratory for testing.
Only by accurately typing the virus or viruses involved in the outbreaks will it be possible to identify the most effective vaccine to use against it.
Food security bulwark
FMD does not pose a direct health threat to humans, but affected animals become too weak to be used to plough the soil or reap harvests, suffer significant weight loss, and produce less milk. Many animals are dying from the disease.
Farm animals are crucial to food security in North Korea. Cows and oxen are primarily used for dairy production and are a key source of draft power in agricultural production. Goats and pigs, also susceptible to FMD, are important source of dairy products and meat.
Current North Korea’s livestock population consists of 577,000 head of cattle, 2.2 million pigs and 3.5 million goats.
FMD affects cattle, buffaloes, sheep, goats, swine and other cloven-hoofed animals. It is highly contagious and spreads through mucus, saliva or body fluids that can contaminate materials such as clothing, crates, truck beds, and hay and be transmitted to other animals.
UPDATE 4 (2011-3-22): Pork prices rising with FMD meat on sale. According to the Daily NK:
With North Korea seemingly unable to bring an outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease centered on the Pyongyang region under control, inside sources have revealed that the price of good pork in the markets is skyrocketing as a result of diminishing supplies, while infected meat is being sold on the quiet for lower prices.
Speaking with The Daily NK on the 22nd, a source from North Pyongan Province explained, “Pork is right now selling for 6,000 won per kilo in the market. The price, which was 2,600 won in the market last December, is climbing all the time, and now is at the point where the average person has no chance of being able to buy it.”
According to sources, the situation is similar in Nampo, where pork was selling for 3,500 won in December, but had reached 6,500 won by February. In Sariwon in North Hwanghae Province, the price had hit 5,000 won by the end of February.
The news of an emerging foot-and-mouth disease problem in North Korea first emerged through sources earlier this year, but the authorities only confirmed it officially and reported control measures via Chosun Central News Agency on February 10th.
According to an official report submitted by the North Korean authorities to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) at around the same time, the outbreak had by then spread to 48 places across much of south and central North Korea, with 15 of those places falling within the Pyongyang administrative region.
The report outlined how North Korea first attempted to combat the outbreak with an indigenously produced vaccine, but this was of limited use. It also noted that official North Korean policy is to bury those animals that die from the disease and quarantine those that are infected.
However, inside sources say that in reality people are digging up buried animals in order to sell the meat in the market at a lower price.
The North Pyongan Province source explained, “Meat infected with foot-and-mouth disease is being sold in the market tacitly; the price of it is somewhat lower. The work of burying pigs with foot-and-mouth disease is being done, he said, but it is said that animals continue to be dug up and are sometimes being sold in the market.”
The source gave the example of a pig farm in Pyongsung, where 6 people dug up previously buried pigs last December to sell in Pyongsung Market. They were selling the meat for 2,000 won/kg, he said, but were caught by the authorities.
The source also revealed that on December 30th, 2010, 500 pigs were buried near Pyongyang, but two days later had disappeared, while in Sinuiju it is said that “If it is buried in the daytime, people say that by that very evening it will appear in the market.”
Of course, the fact is that the North Korean authorities are unable to put in place an efficacious policy to combat the outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease or the selling on of infected meat, not least because persons caught for selling infected meat can simply navigate their way out of trouble and go back to their activities.
UPDATE 3 (2011-3-2): A UN FAO team is in the DPRK to inspect the foot-and-mouth outbreak. According to the Joongang Ilbo:
An official at the FAO was quoted by RFA as saying that the scale and variety of the aid would be determined after discussions with North Korean government officials. The exact itinerary of the group was not released.
The UN food agency also said that along with the team that arrived in North Korea last month, additional officials, including an expert on contagious diseases, would be sent to the area.
The South Korean government has said that it has been monitoring the development of the outbreak. However, the South Korean Ministry of Unification said after North Korea’s official report on the disease that Pyongyang has not made any requests for aid nor did Seoul have plans to offer any assistance.
North Korea announced on Feb. 10 that over 10,000 pigs and cattle had been infected with FMD, prompting North Korean officials to alert the UN of the outbreak.
The North struggled with FMD cases in 2007 and 2008, which led to the culling of thousands of pigs and cattle. During those episodes, the FAO and the South Korean government provided aid.
UPDATE 2 (2011-2-27): The Daily NK reports that the OIE report shows animals are not being culled:
Unlike in 2007, when North Korea reacted swiftly to an outbreak of the disease by culling animals, this time the authorities appear to have reacted poorly despite the fact that the disease has now been found at more than 48 locations in Pyongyang City and Pyongan, Hwanghae and Kangwon Provinces.
According to an OiE report derived from the letter, in which the North finally confirmed the rumored outbreak after a month of silence, Pyongyang has apparently tried to address the situation using a combination of disinfection measures and a domestically produced vaccine, but this has met with little success.
“Given the number of livestock which have died of foot-and-mouth disease, it is uncertain just how far the infection has spread,” Korea Rural Economic Institute Vice-President Kwon Tae Jin explained to The Daily NK. “The small number of infected heads of cattle reported by North Korea is also difficult to accept at face value.”
“If the North Korean authorities have not destroyed the infected cows and pigs in the hope that they will recover, then it is a serious problem. It means we have no idea how far the disease has spread,” Kwon added.
15 of the existing locations in which the disease has so far been detected are in Pyongyang and surrounding areas. In order to combat the spread of the disease to other regions, the authorities are said to have implemented across-the-board restrictions on movement into and out of the city.
However, news of the disease has still not been reported officially, and domestic sources have told The Daily NK that they have not heard anything about it to date.
UPDATE 1 (2011-2-18): DPRK report (below) shows extensive damage from foot-and-mouth disease. According to Yonhap:
North Korea has reported to a global animal health agency that it had suffered a total of 48 outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) since Christmas last year.
The impoverished communist state made the report to the Paris-based World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) on Feb. 8, saying about half of 17,522 “susceptible” pigs had died from the disease.
Only 3 percent of 1,403 cows suspected of being infected had died from the disease, according to the report posted on the OIE Web site, while none of the 165 susceptible goats had died.
At the time the report was filed, no livestock were yet culled as a preventive measure, according to the report created by Ri Kyong-gun, a quarantine director for the Ministry of Agriculture. A map of outbreaks showed the disease had spread out over almost half of North Korea.
“Vaccination has been applied with a locally developed vaccine but was not effective to control the disease,” the report said, adding that the origin of the outbreak remains “unknown or inconclusive.”
North Korea has banned the inflow of pork and beef from South Korea since late last year for fear that the disease — rampant south of the heavily armed border — may spread there.
Despite the measure, the North, which suffers serious food shortages, reported the outbreak to the United Nation’s Food and Agriculture Organization earlier this year.
The country said in the OIE report that it has restricted movement and conducted “disinfection of infected premises and establishments” to fight the spread of the animal disease.
In 2007, North Korea suffered similar outbreaks, prompting South Korea to dispatch a team of animal health experts amid a mood of reconciliation.
FMD is highly contagious and affects cloven-hoofed animals like cattle, pigs, deer, goats and sheep. The disease causes blisters on the mouth and feet of livestock and leads to death. It is rarely transmitted to humans.
ORIGINAL POST (2011-2-18): Below is a map and list of reported foot and mouth disease outbreaks in the DPRK:
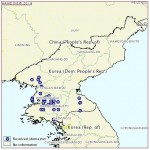
The World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) has reported 48 outbreaks of foot and mouth disease (FMD) in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea.
The outbreaks are located in:
–Kangwon (Anbyon, Kimhwa, Phangyo, Phyonggang)
–Kumgang
–Pyongyang (Sadong, Ryokpo, Rakrang, Kangdong, Mangyongdae)
–Nampho (Nampho and Kangso)
–North Hwanghae (Kangnam, Sangwon, Hwangju, Yonsan, Sinphyong, Suan, Songrim)
–North Pyongan (Thaechon, Pakchon)
–South Hwanghae (Chongdan)
–South Pyongan (Anju, Phyongwon)
The OIE posted a report developed from an official letter sent by the DPRK dated 7 February 2011 and received on 8 February 2011. You can see the OIE report here.