Daily NK
Lee Sung Jin
10/22/2007
(Click on image for original size)
 According to DailyNK’s research on prices in North Korea conducted in late September, the prices in Pyongyang are similar to the prices in other parts of the country. The finding shows that Jangmadang (markets) economy has been going through integration and similar distribution process across North Korea.
According to DailyNK’s research on prices in North Korea conducted in late September, the prices in Pyongyang are similar to the prices in other parts of the country. The finding shows that Jangmadang (markets) economy has been going through integration and similar distribution process across North Korea.
In the past, domestic commodities were sold cheap, and foreign products were sold expensive in Pyongyang.
DailyNK has been conducting quarterly research on prices in the central such as Pyongan Province and Hamkyung Province and northern areas.
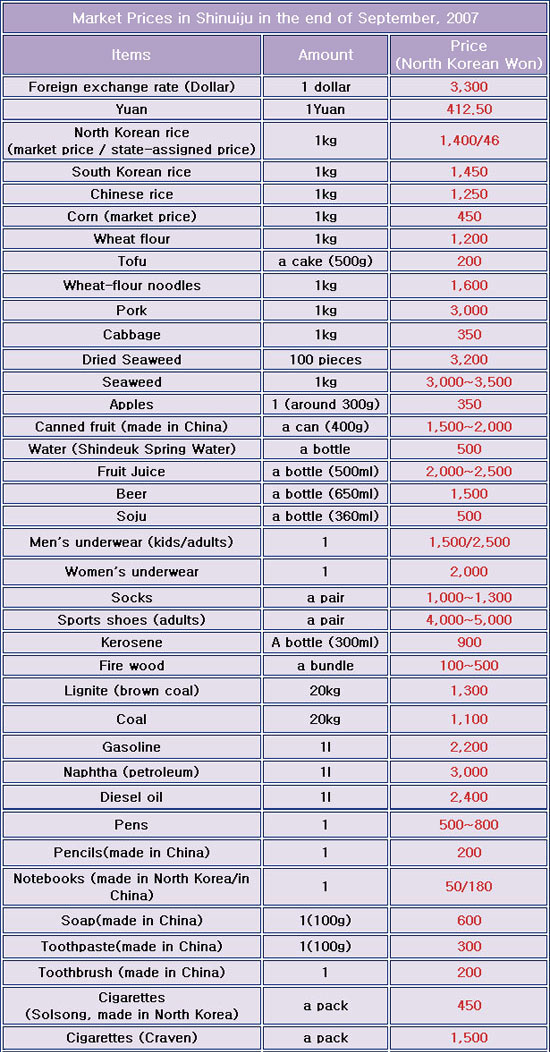
This time the research result shows that the price of rice in a Jangmadang in Pyongyang is 1,350 won/kg, which is similar to the price of rice in Sinuiju, 1,400won/kg. In North Korea, the rice price serves as a gauge for price trends.
In Pyongyang, the exchange rate is about 330 thousands won to 100 dollars, which is the same as the exchange rate in other places. The most famous imported cigarettes, Cat (Craven A) is sold at the same cost of 1,500 won in Pyongyang and other areas.
Subsidiary food is more expensive in Pyongyang. The price of cabbage is 400 won/kg, 50 won/kg higher than cabbage price in Sinuiju. The price of pork ranges from 3,500 to 4,000/kg, 500~1,000 won/kg higher than the pork price in other areas.
The prices of seafood such as brown and green seaweed, and dried Pollack are cheaper in Pyongyang. Seafood caught in Kangwon Province and neighboring areas is transported to markets in Pyongyang in refrigerator car. Since the demand is high, seafood is sold in great quantities, and the price remains low in general.
Movie ticket prices range from 200 to 400 won. Telephone service is charged five won per minute. Overall, the price range for each commodity is high, and many different kinds of goods are available in Jangmadang.
Imported items from China such as socks, sports shoes, or underwear are expensive being sold at a cost of 1,000 won in Pyongyang. That is because there are extra shipping rates and labor costs imposed on Chinese goods transported to Pyongyang. On the contrary, in Sinuiju, imported goods from China are circulated on the market right away.
Often, retail prices are higher in Pyongyang because of high levels of consumption among Pyongyang citizens. However, cigarettes or liquor produced in Pyongyang, or clothes from South Korea circulated to other areas via Pyongyang are sold cheap in Pyongyang.
However, in these days the differences in regional price levels have almost disappeared.
A defector from Pyongyang, Ahn Chul Min (a pseudonym) who came to South Korea in 2006 said, “Prior to 2002, there were individuals who hung around from place to place and made money on price differences. But nowadays, the retail prices are almost uniform across the country because people just use a telephone and find out where to get items they want at what prices.
“Since there is no big difference in retail prices, retailers are not doing well in business,” Ahn added, “Instead, individuals driving a truck and selling goods wholesale are making good money.”
Ahn said, “Not everyone who lives in Pyongyang is well-to-do. Despite of their locations whether in Pyongyang or Chongjin, all markets have goods from South Korea and China. The poor people even if they live in Pyongyang should buy cheap and low quality of products from China. In contrast, those who live in Chongjin and have money can buy goods from South Korea anytime.”
Market Prices Consistent Throughout DPRK
Institute for Far Eastern Studies (IFES)
NK Brief No. 07-10-25-1
10/25/2007
The results of a survey conducted by Daily NK on the price of goods in Pyongyang at the end of September show that prices in the capital were similar to those in rural areas. This is an indication that markets throughout the country are integrated, and evidence that goods can be circulated from region to region.
In the past, the price of domestic goods in Pyongyang was relatively cheep, while imported goods were sold at high prices. During that time, Daily NK carried out local price surveys in central regions such as Pyongan and Hamkyung provinces, as well as in northern areas. According to this latest survey in Pyongyang, the cost of one Kg of rice, the standard measure of the cost of goods in North Korea, was 1,350 won, similar to the 1,400 won price in Sinuiju, and the 1,250 won cost in Hyeryung. An exchange rate of 3,300 won per USD is also in line with rural exchange rates, as is the 1,500 won price tag on a pack of Craven A cigarettes, the most favored imported cigarette in North Korea.
Non-essential food goods are more expensive in Pyongyang than in outlying areas, with one Kg of lettuce selling for 400 won, 50 won more than in Sinuiju. Also, pork in the capital runs between 3,500 and 4,000 won per Kg, which is 500 to 1,000 won more than it would cost elsewhere in the country.
On the other hand, seaweed, dried Pollack, and other marine products are cheaper in Pyongyang than elsewhere. Ocean harvests from Kangwon and neighboring provinces are brought to Pyongyang markets by way of refrigerated trucks. Because of high demand, a variety of goods get delivered, yet overall, prices are held fairly low.
Overall, the price range on a particular ware was very wide, indicating that there was a variety of products available in the markets. The survey found that goods such as undergarments, socks, sneakers imported from China were selling for the high cost of 1,000 won each. In Sinuiju and other northern areas, goods from China are brought directly to markets, but by the time these same goods reach Pyongyang, additional labor and transportation costs force prices up. Pyongyang residents typically have more money to spend than those in rural areas, also leading vendors to raise prices on some goods, however cigarettes and alcohol produced in Pyongyang and distributed to rural areas, as well as South Korean goods which reach DPRK markets by way of Pyongyang, are slightly less expensive in the capital.
Recently, regional price differences have nearly disappeared. Prior to 2002, some traders earned their living traveling from region to region exploiting price differences. However, now with one simple phone call, North Koreans can find out where and for what price goods are being sold, leading the majority of retail prices to be similar throughout the country.