UPDATE 4 (2014-10-23): Here is coverage in the Choson Ilbo:
North Korea signed US$1.3 billion worth of investment deals with Chinese businesses at a trade fair in the Chinese border city of Dandong last week.
China’s Xinhua news agency on Monday quoted one of the organizers of the trade fair as saying, “North Korean and Chinese businesses signed letters of intent covering 60 trade and investment pacts amounting to $1.26 billion.
“Another eight letters of intent were signed between North Korea and businesses in other countries involving $11.6 million worth of trade and $100 million worth of investments.”
Around 500 North Korean officials attended the trade fair, including those in charge of economic development.
But the amount of deals struck was smaller than last year (93 deals worth $1.6 billion), due to deteriorating relations between Beijing and Pyongyang.
Skeptics also point out there is no guarantee that the letters of intent will materialize into concrete investments.
UPDATE 3 (2014-10-20): Here is additional coverage by Yonhap:
In an apparent bid to lure Chinese investors, North Korea has publicized somewhat detailed information about its workforce during an annual trade with China, boasting of a well-educated pool of labor.
The North’s National Economic Development General Bureau released a booklet to show off its labor force at the five-day trade fair, which ended on Monday in the Chinese border city of Dandong.
According to the booklet, North Korea’s total population stood at 24.34 million as of last year. About 12.17 million people constituted a “prepared labor force that can adapt to randomly-chosen professions,” according to the booklet.
North Korea also boasted that it extended compulsory education by one year to 12 years from this year.
“In our country, the level of education is high and the potential of intellectual capability is solidly prepared,” the booklet said. “There is no unemployment, labor striking or sabotage in our country.”
North Korea sent 68 business entities to this year’s North Korea-China Economic, Trade, Culture and Tourism Expo, the third of its kind, down about 30 percent from last year.
The decline in North Korea’s participation at this year’s show underscored the continued strain in bilateral relations, particularly since the North’s third nuclear test in February last year and the execution of the North Korean leader Kim Jong-un’s once-powerful uncle, Jang Song-thaek, who had close ties with Beijing.
UPDATE 2 (2014-10-20): Here is coverage from Xinhua:
A 500-strong trade delegation from the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) is promoting the country’s investment opportunities at a four-day expo in China’s border city of Dandong, Liaoning Province.
The third China-DPRK Economic, Culture and Tourism Expo, closing on Tuesday, has seen 70 million yuan (about 11.6 million U.S. dollars) of trading, agreements on eight investment contracts worth 100 million U.S. dollars, and 60 trade agreements worth 1.26 billion U.S. dollars in total.
Shi Guang, mayor of Dandong, said the expo has drawn 100 DPRK exhibitors, 96 companies from Russia, India, China’s Taiwan and Hong Kong, as well 210 companies from the Chinese mainland. About 250,000 visitors from 20 countries and regions have attended.
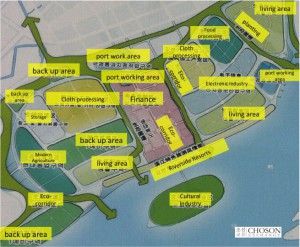
The DPRK is developing a Special Economic Zone to help implement its opening-up policy.
Kim Jong Sik, an official with the DPRK Economic Development Association,ssaid the zone is open up to any countries interested in establishing economic and trade relations with the DPRK.
The zone will be dedicated to external trade, assimilating foreign investment and improving the country’s economy, he said.
According to the official, the DPRK has clinched bilateral trade and investment protection agreements with more than 30 countries and mapped out an economic structure including metallurgy, mining, production of construction materials, machinery, garment making, shipbuilding, agriculture and aquaculture.
Kim said the country’s human resources, environment and tourist resources are key factors to appeal to foreign investment. It has been working to optimize investment laws.
The city of Dandong faces the DPRK across the Yalu River. Construction of a bridge linking both sides has been basically completed. It is expected to help facilitate the DPRK’s exchanges with the outside world.
UPDATE 1 (2014-10-18): According to Yonhap:
North Korea is still showing off its products at an annual trade fair with China, but the number of North Korean business entities attending the event this year was about 30 percent less than last year.
The mood is subdued at the five-day trade fair in the Chinese border city of Dandong, reflecting strained political ties between North Korea and China amid Beijing’s signals of displeasure with Pyongyang’s nuclear ambition.
Organizers had said that about 100 North Korean business entities would attend the annual exhibition, but only 68 of them actually attended this year’s event. About 100 North Korean business entities attended last year’s exhibition.
The crowd was also noticeably smaller than it was last year.
“This year, we didn’t bring many products. Instead of selling products, we come here with hopes to meet with Chinese people who want to invest in our factory,” said an official at a North Korean trading firm who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
The decline in North Korea’s participation at the North Korea-China Economic, Trade, Culture and Tourism Expo, which began its five-day run Thursday, underscored the continued strain in bilateral relations, particularly after the North’s third nuclear test in February last year and the execution of the North Korean leader Kim Jong-un’s once-powerful uncle, Jang Song-thaek, who had close ties with Beijing.
In what many analysts believe was a message to North Korea, Chinese President Xi Jinping paid a two-day visit to South Korea in July this year, breaking a long-standing tradition by Chinese heads of state of visiting Pyongyang before Seoul.
North Korea’s bilateral trade with China stood at US$4.05 billion in the first eight months of this year, down 1.1 percent from the same period last year, according to Chinese customs data.
Economic development, along with the expansion of its nuclear capability, has been a new focus of North Korea’s policy under young leader Kim Jong-un, who took over in late 2011 after his father, Kim Jong-il, died.
North Korea, beset by poor infrastructure and international sanctions over its nuclear and missile programs, has announced plans to set up an economic development zone in each of its provinces.
Despite sanctions that discourage foreign investment, Kim Jong-sik, an official at the North’s National Economic Development General Bureau, told an audience at the exhibition that Pyongyang would set up a “one-stop service” that makes it easier for foreigners to invest in the country.
“With regard to economic development zones, we will simplify immigration procedures and build a one-stop service, which has been widely introduced around the world, to try to fully guarantee conveniences of foreign investors,” Kim said.
ORIGINAL POST (2014-10-16): According to Yonhap:
North Korea and China kicked off an annual trade exhibition on Thursday, with about 2,000 Chinese companies attending, organizers said.
The five-day trade fair in the Chinese border city of Dandong, where more than 70 percent of bilateral trade between the two nations is conducted, suggests economic ties between Beijing and Pyongyang remain largely unaffected despite the North’s nuclear and missile programs.
About 100 North Korean business entities will attend the North Korea-China Economic, Trade, Culture and Tourism Expo, the third of its kind.
At last year’s exhibition, North Korea and China signed 93 preliminary deals worth US$1.6 billion. It has not been confirmed whether the deals usually lead to actual shipments.
Besides North Korea and China, companies from Hong Kong, Russia, Thailand and Taiwan will join this year’s exhibition, organizers said.
North Korea’s bilateral trade with China stood at US$4.05 billion in the first eight months of this year, down 1.1 percent from the same period last year, according to Chinese customs data.
North Korea’s exports to China declined 0.8 percent on-year to $1.84 billion during the eight-month period, while imports fell 1.2 percent to $2.21 billion, the data showed.
Here is coverage of the first and second expo.
Read the full story here:
N. Korea, China kick off annual trade fair
Yonhap
2014-10-16