By: Benjamin Katzeff Silberstein
Given the self-imposed border lockdown North Korea is under at the moment, the recent rise in food prices should come as no surprise. The precise factors are difficult to pin down, but whatever they are, there is some serious cause for concern.
The main reason is the rapid rise in the price of corn as of late. One Daily NK-source in North Korea attributes it to large-scale state purchases of corn for snacks manufacturing in honor of Kim Jong-il’s birthday on February 16th.
The article makes clear, however, that this is only a partial explanation. Indeed, looking at the price index, it’s clear that the rise started long before February. On November 15th last year, the average price for a kilo of corn was 1350 won. On February 23rd this year, the average price was 3137 won. That’s a rise of 135 percent in a relatively short period of time. Prices of corn have often risen in the beginning part of the year, but not by this much.
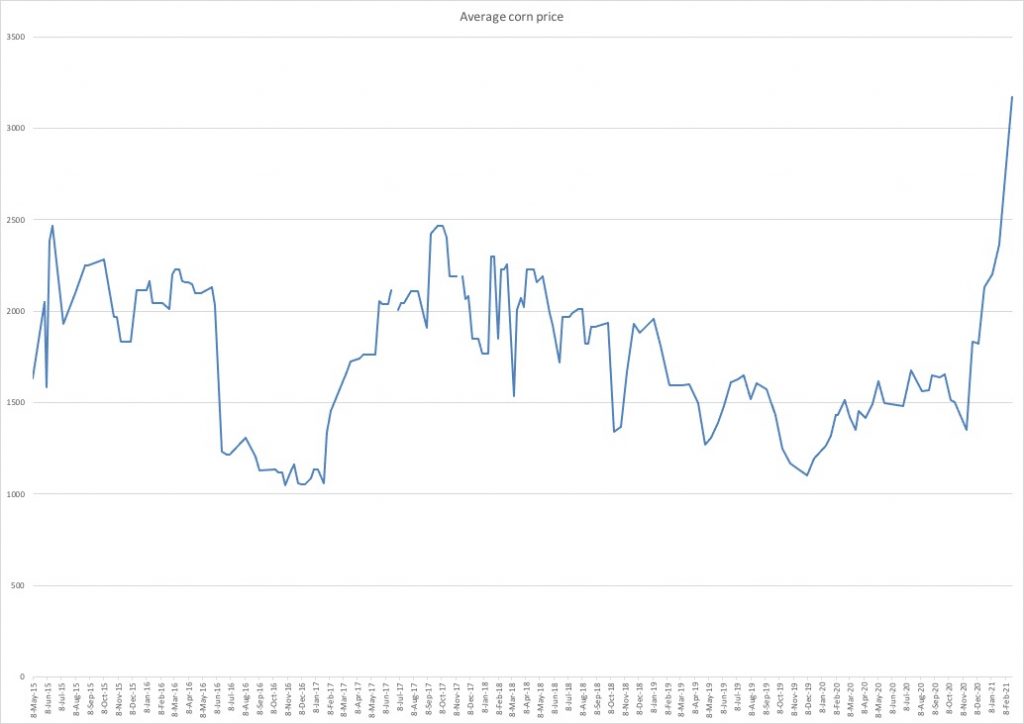
Average corn prices in Pyongyang, Sinuiju and Hyesan, from 2015 and onward. Graph by NKEconWatch, data source: Daily NK.
Looking at individual cities, the rise is even more staggering. In Hyesan, where food prices tend to be higher in general, corn prices rose from 1450 won/kilo on November 15th last year to 3620/kilo on February 23rd. That’s an increase of 150 percent in only a few months.
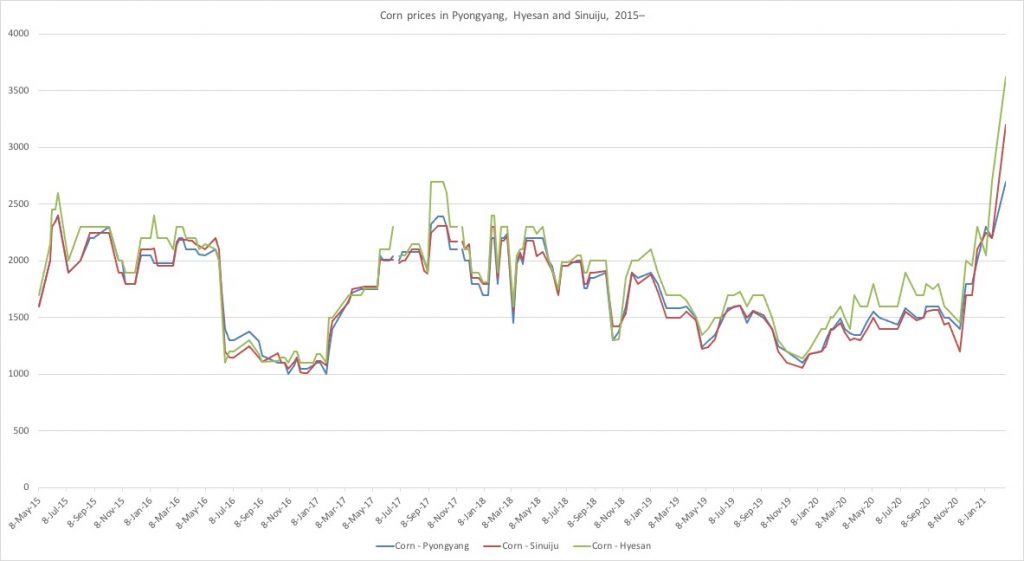
Corn prices in Pyongyang, Sinuiju and Hyesan, from 2015 and onward. Graph by NKEconWatch, data source: Daily NK.
Why is this a concerning development for corn prices specifically?
First, corn is, in the North Korean context, rice’s less desired sibling. Corn always makes up a significant part of the diet for a big proportion of the North Korean population. However, when food becomes more scarce, people switch over a larger portion of their diets to corn, since it gives more food for the same amount of money. So a rise in corn prices may be a signal of growing scarcity overall.
Second, even if a large proportion of the rise was indeed caused by increasing state purchases, this is also a troubling indicator for the state of the North Korean market for food. If state procurement for snacks manufacturing for one single day can impact prices so much, this suggests a market under considerable stress and volatility to begin with.
At the same time, rice prices have remained conspicuously low and stabile. Rice prices in the last observation in the price index are around their seasonal normal. I’d be careful to assume too much based on this, however. Rice prices are lower right now than around the same time last year. This may – and I want to stress how little we know for certain – indicate that they are in fact lower not because supply is stabile, but because demand is lower. More consumers switching over their consumption to cheaper foods such as corn would put downward pressure on rice prices.
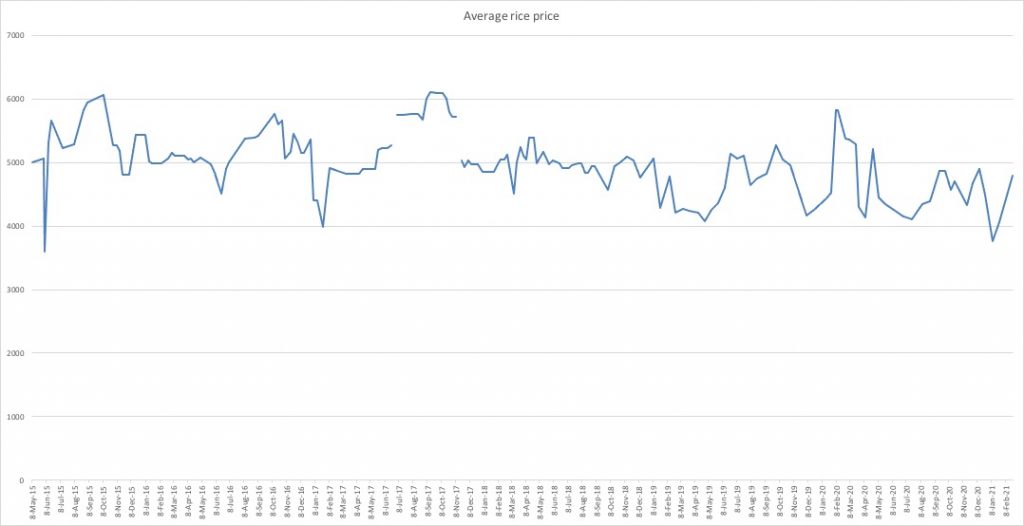
Average rice prices in Pyongyang, Sinuiju and Hyesan, from 2015 and onward. Graph by NKEconWatch, data source: Daily NK.
The current situation will only be possible to fully evaluate in a few weeks when we have more data points available. Suffice to say for now that, with all the caveats about the trappings of data from North Korea, the situation looks concerning.
Update March 16th, 2021: DailyNK recently published more info about the corn price situation, reporting that prices have stabilized in much of the country. Still, 3,000 KWP/kg, reported in “other inland regions” (than Hyesan), is high. It’s more than double the average price reported in Daily NK’s price index around one year ago.
