By: Benjamin Katzeff Silberstein
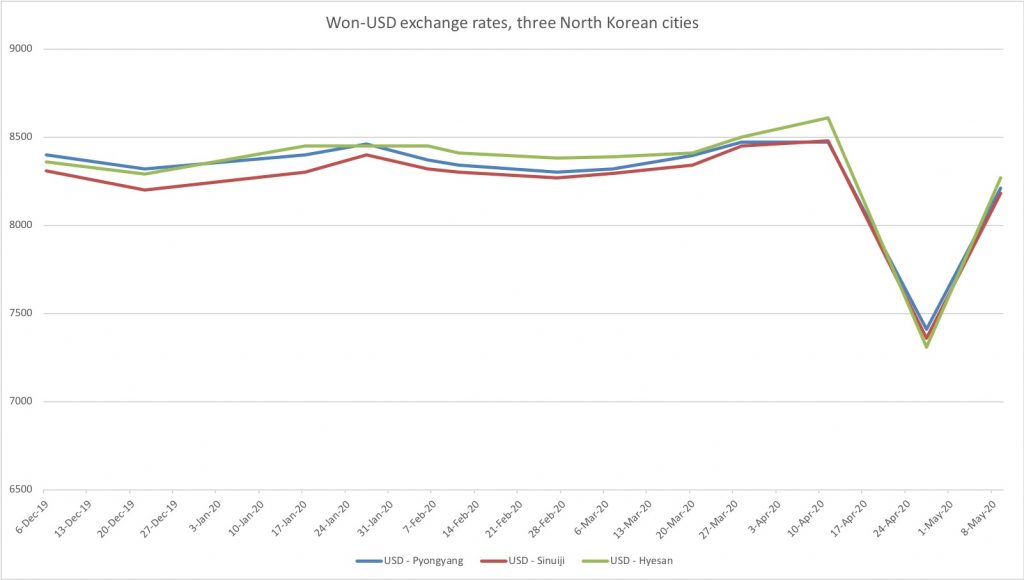
New market prices for North Korea came out recently, and lots is happening. Rice prices are down significantly, but compared to last year, the levels so far are quite normal. We should expect them to rise as the country goes further into the lean season between May and September (roughly). Foreign exchange rates, perhaps most interestingly, are fluctuating quite significantly, and the dollar especially so. The USD took a dive late last month, but it’s been fluctuating quite significantly before that as well, which would be more visible if not for the recent dive in the graph:
It seems that uncertainty itself is one of the main reasons. One in-country source told Daily NK:
“Even ordinary sellers who have long conducted relatively stable transactions in foreign currency are now afraid of losses because of dramatic fluctuations in the exchange rate,” the source told Daily NK. “Recently, the changes have been so frenzied that it’s not exaggerating to say that the prices in the afternoon will be different from the prices in the morning.”
“Wholesalers at the Pyongsong Market whose main patrons are other wholesalers throughout the country are complaining about the impact of the fluctuations in the exchange rate,” continued the source. “There are such major changes in the exchange rate between when wholesalers receive goods and then pass them along to retailers that uncertainty prevails.”
Citing exchange rate fluctuations of around KPW 1,000 in the past, some people reportedly do not believe that the fluctuations are a big deal. Yet, “most people think that we can’t sit idly by because the prices of imported goods are [also] increasing,” the source said.
“The damage done to businesses due to the exchange rate [fluctuations] and the increase in commodity prices are making things difficult for those who deal with transactions in foreign currency,” he added.
(Source: Kang Mi Jin, “Fluctuating exchange rates cause headaches for N. Korea’s business people,” Daily NK, 19/7/2020.)
It’s not just the government’s Covid19-measures themselves, such as the border closure, that impact the exchange rate. As noted on this website yesterday, the state is taking coercive actions of various forms to bring in funds, such as reportedly banning the use of foreign currency for domestic transactions in the hope that people will see no choice but to exchange their foreign money for domestic, bringing in much needed foreign exchange to the state.